OR gate: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "{| class="wikitable floatright" style="text-align:center" |- ! colspan="3" | OR gate truth table |- bgcolor="#ddeeff" |colspan=2|'''Input''' || '''Output''' |- bgcolor="#ddeeff" | A || B || A OR B |- |{{no2|0}} || {{no2|0}} || {{no2|0}} |- |{{no2|0}} || {{yes2|1}} || {{yes2|1}} |- |{{yes2|1}} || {{no2|0}} || {{yes2|1}} |- |{{yes2|1}} || {{yes2|1}} || {{yes2|1}} |} In digital electronics, an '''OR gate''' is a logic gate which produces an output of true when a...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Logic == | == Logic == | ||
A two-input OR gate can be expressed in [[Boolean logic]] as <math>A + B</math> or <math>A \lor B</math>. | A two-input OR gate can be expressed in [[Boolean logic]] as <math>A + B</math> or <math>A \lor B</math>. | ||
= Alternatives = | |||
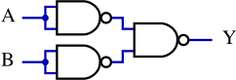
If a specific type of gate is not available, a circuit that implements the same function can be constructed from other available gates. Through the use of the "universal" [[NAND gate|NAND gates]] and [[NOR gate|NOR gates]], almost any other Boolean logic gate can be constructed. | |||
An OR gate can be constructed using three NAND gates or two NOR gates in the following topologies: | |||
{| | |||
![[File:OR from NAND ANSI.svg|236x236px]] | |||
![[File:OR from NOR ANSI.svg|251x251px]] | |||
|} | |||
{{Stub}} | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Latest revision as of 19:35, 8 November 2023
| OR gate truth table | ||
|---|---|---|
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | A OR B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
In digital electronics, an OR gate is a logic gate which produces an output of true when any of its inputs are true. A LOW (0) output results when all of the inputs to the gate are LOW; if any of the inputs are HIGH (1), a high output results.
Logic
A two-input OR gate can be expressed in Boolean logic as or .
Alternatives
If a specific type of gate is not available, a circuit that implements the same function can be constructed from other available gates. Through the use of the "universal" NAND gates and NOR gates, almost any other Boolean logic gate can be constructed.
An OR gate can be constructed using three NAND gates or two NOR gates in the following topologies:
|

|
|---|

